Aug . 13, 2024 20:56 Back to list
Comprehensive Guide to Brake Drum Specifications for Optimal Vehicle Performance and Safety
Understanding Brake Drum Specification A Comprehensive Guide
Brake drums are essential components of a vehicle's braking system, providing the necessary friction to slow down or stop the vehicle safely. Selecting the right brake drum not only ensures proper functionality but also contributes to overall vehicle safety. In this article, we will delve into the critical elements of brake drum specifications, helping technicians and automotive enthusiasts make informed decisions.
Importance of Brake Drums
Brake drums are typically used in drum brake systems, which consist of several key components the drum itself, brake shoes, and a wheel cylinder. When the brake pedal is engaged, hydraulic pressure pushes the brake shoes against the inner surface of the drum, creating friction that slows the vehicle. Over time, brake drums can wear down, leading to decreased performance and safety hazards if not replaced or maintained appropriately.
Key Specifications to Consider
1. Material Composition Brake drums are primarily made from cast iron or aluminum alloy. Cast iron offers excellent heat dissipation and durability, making it a popular choice for heavier vehicles. Aluminum drums, while lighter and resistant to corrosion, may be suited for specific applications or performance vehicles. It’s crucial to select a material that aligns with your vehicle’s requirements.
2. Diameter and Width The diameter and width of the brake drum affect the overall braking performance. Larger drums provide more surface area for the shoes to make contact, improving braking efficiency. Conversely, narrower drums may limit performance but can be lighter, which is beneficial for certain performance vehicles. Always ensure that the specified sizes align with the vehicle’s requirements.
brake drum specification guide
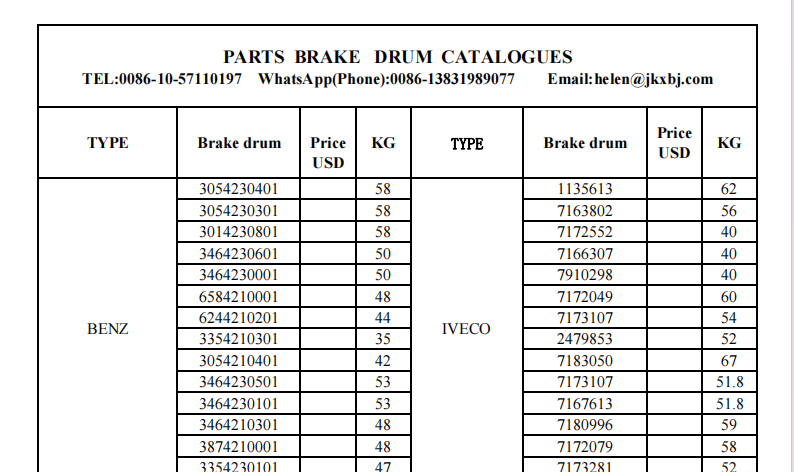
3. Thickness and Minimum Specification Each brake drum has a specified thickness that must be adhered to for safe operation. As the drum wears down through usage, it must be replaced before it reaches its minimum thickness, which is usually stamped on the drum itself. Operating with drums below this thickness can lead to brake failure due to overheating and reduced surface area for friction.
4. Drum Shape and Design Most brake drums feature a curved design, which contributes to even pressure distribution when the brake shoes engage. Some drums may also have a vented or non-vented design. Vented drums allow for better heat dissipation, while non-vented drums may be more compact but could lead to overheating in high-performance scenarios.
5. Compatibility and Interchangeability It is vital to ensure that the selected brake drum is compatible with your vehicle’s make and model. Interchangeability can often lead to performance issues or safety hazards if wrong parts are used. Always refer to the manufacturer’s specifications or consult an expert for guidance.
Maintenance and Inspection
Regular maintenance of brake drums is crucial to ensure optimal performance and safety. Technicians should routinely inspect the drums for signs of wear, such as grooves, cracks, or excessive heat discoloration. Properly maintained drums will not only enhance braking efficiency but also extend the lifespan of associated components, such as brake shoes.
Conclusion
Understanding brake drum specifications is essential for any automotive technician or enthusiast. By considering factors such as material, dimensions, thickness, design, and compatibility, one can make informed decisions that enhance vehicle safety and performance. Regular inspections and adherence to manufacturer guidelines will ensure that your braking system remains effective, providing peace of mind on the road. Select wisely, maintain diligently, and drive safely.
-
Brake Drum Man - High-Quality Drum Brake Drums & Brake Shoes for Reliable Performance
NewsJun.24,2025
-
High-Quality Brake Drum Kamaz – Durable Drum Brake Drum & Brake Shoe Replacement
NewsJun.10,2025
-
High-Quality Brake Drum Liza for Drum Brake Systems - Superior Durability and Performance
NewsJun.10,2025
-
High-Quality Brake Drum Kamaz – Durable Drum Brake Drum & Brake Shoe Solutions
NewsJun.10,2025
-
Durable Kamaz Brake Drums High-Performance Truck Parts
NewsJun.09,2025
-
Premium Brake Drum Maz Kit with Shoes Enhanced Braking
NewsJun.09,2025
