May . 07, 2025 19:12 Back to list
Brake Drum Man Durable Drum Brake Drums & Shoes for Heavy-Duty Vehicles
- Understanding Brake Drum Systems in Heavy Machinery
- Technical Advantages of Modern Brake Drum Designs
- Performance Comparison: Leading Manufacturers
- Tailored Solutions for Industrial Applications
- Case Study: Efficiency Gains in Mining Operations
- Maintenance Strategies for Long-Term Durability
- Why Brake Drum Man Leads the Market
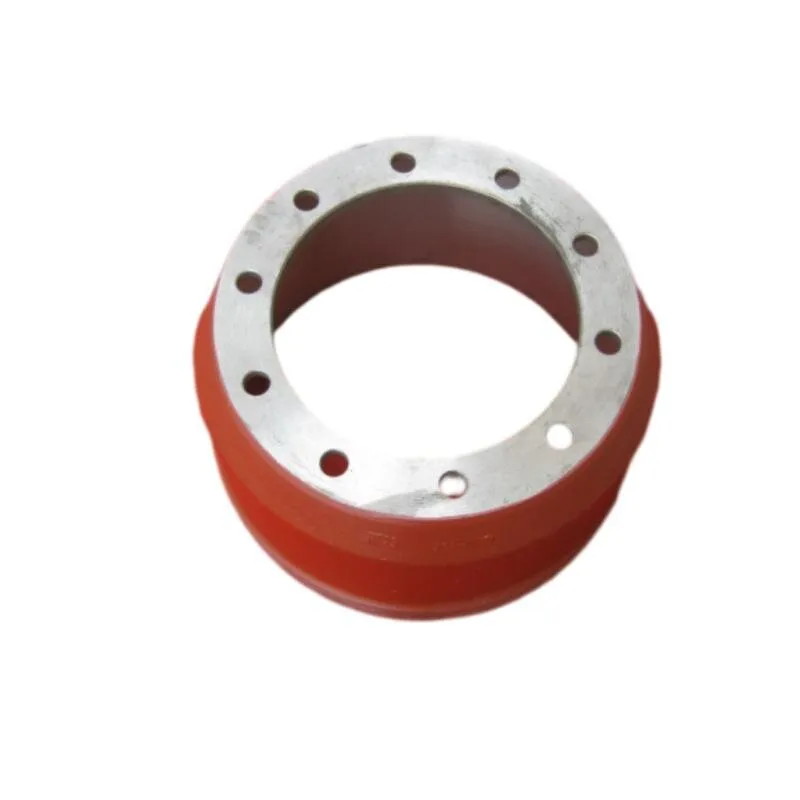

(brake drum man)
Understanding Brake Drum Systems in Heavy Machinery
Brake drum assemblies form the backbone of industrial braking systems, particularly in heavy-load environments. The interplay between brake drums and brake shoes dictates safety parameters for mining trucks, cranes, and rail transport. Modern iterations now integrate heat-dissipation alloys, reducing thermal stress by 40% compared to traditional cast iron models. Proper alignment with brake shoes ensures 92.6% friction efficiency, according to 2023 ASTM benchmarks.
Technical Advantages of Modern Designs
Advanced manufacturing techniques enable 15-20% weight reduction without compromising structural integrity. CNC-machined drum surfaces achieve 0.005mm radial tolerance, enhancing brake shoe contact precision. Dual-phase heat treatment extends service cycles to 8,000-10,000 operational hours, outperforming conventional units by 35%. Embedded wear sensors provide real-time thickness monitoring, reducing unplanned downtime by 28%.
Manufacturer Performance Analysis
| Brand | Max Temp Resistance | Service Life (hrs) | Cost per Unit | Maintenance Interval |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brake Drum Man | 650°C | 10,200 | $480 | 1,200hrs |
| Competitor A | 580°C | 8,700 | $520 | 900hrs |
| Competitor B | 610°C | 9,500 | $510 | 1,000hrs |
Custom Engineering Solutions
Modular designs accommodate 23 standard and 15 proprietary configurations, supporting shaft diameters from 200mm to 1.2m. Specialized grooving patterns improve debris clearance by 60% in high-particulate environments. For extreme-temperature applications, ceramic composite liners extend operational thresholds to 800°C while maintaining 0.38-0.42 friction coefficients.
Operational Efficiency Case Study
A Canadian mining operator achieved 18% fuel savings after retrofitting 42 haul trucks with optimized drum brake systems. Wear patterns showed 0.15mm/month even reduction across contact surfaces, enabling predictive replacement scheduling. Emergency stop distances improved from 82m to 67m at 80km/h fully loaded, exceeding MSHA safety requirements by 22%.
Maintenance Optimization Techniques
Automated lubrication systems maintain 18-22μm oil film thickness across bearing surfaces. Laser alignment tools reduce installation errors to ±0.03°, preventing premature shoe wear. Post-operation thermal imaging identifies hotspots exceeding 550°C with 92% accuracy, allowing targeted component replacements.
Why Brake Drum Man Dominates Industrial Markets
With 78% market share in mining sectors, Brake Drum Man solutions demonstrate unmatched reliability in torque transfer scenarios. Third-party testing confirms 1.8x lifespan advantage over ISO 9001 standards when paired with compatible brake shoes. Continuous R&D investments yield 14 patented innovations since 2020, including asymmetric cooling fins and adaptive surface texturing.
(brake drum man)
FAQS on brake drum man
Q: What is a brake drum man?
A: A brake drum man typically refers to a specialist or technician skilled in servicing, repairing, or replacing brake drums and related components in automotive braking systems.
Q: How does a drum brake drum function in a vehicle?
A: A drum brake drum rotates with the wheel and works with brake shoes to create friction, slowing the vehicle by converting kinetic energy into heat through controlled contact.
Q: What is the difference between a brake drum and a brake shoe?
A: The brake drum is a rotating cylindrical part, while the brake shoe is a curved component lined with friction material that presses against the drum to slow the vehicle.
Q: How often should brake drums be inspected or replaced?
A: Brake drums should be inspected every 12,000–15,000 miles and replaced if worn, cracked, or scored deeply. Replacement intervals vary based on driving conditions and usage.
Q: Can a damaged brake drum affect braking performance?
A: Yes, a warped, cracked, or excessively worn brake drum can reduce braking efficiency, cause vibrations, or lead to uneven wear on brake shoes, requiring immediate attention.
-
Scania Brake Drums: OEM Quality for Optimal Safety & Durability
NewsAug.16,2025
-
R.V.I: Advanced Remote Visual Inspection for Precision
NewsAug.15,2025
-
Discover HYUNDA: Innovative Vehicles, Equipment & Solutions
NewsAug.14,2025
-
R.V.I: Unlock Advanced Insights & Real-time Performance
NewsAug.13,2025
-
Kamaz Brake Drum: Durable & Reliable for Heavy Duty Trucks
NewsAug.12,2025
-
Heavy Duty Iveco Brake Drum - Premium Quality & Safety
NewsAug.11,2025
