Dec . 10, 2024 13:11 Back to list
brake drums or discs must
The Importance of Brake Drums and Discs in Vehicle Safety
When it comes to vehicle safety, few components are as critical as the braking system. Integral to this system are the brake drums and discs, which play a significant role in stopping a vehicle effectively. Understanding these components and their functions can help drivers make informed decisions regarding maintenance and replacement, ultimately enhancing safety on the road.
Brake Drums vs
. Brake DiscsBrake systems can primarily be categorized into two types drum brakes and disc brakes. Drum brakes, invented in the late 19th century, consist of a cylindrical drum that rotates with the wheel. Inside the drum, brake shoes are pressed outward against the drum's inner surface when the brakes are applied, creating friction that slows down the vehicle. While drum brakes are still commonly used in some rear braking systems, particularly in larger vehicles, their effectiveness can diminish under high-stress situations—such as in heavy braking or high-speed scenarios.
Conversely, disc brakes feature a flat, disc-shaped rotor that rotates alongside the wheel. When the brakes are engaged, calipers squeeze the brake pads against the rotor, creating friction and bringing the vehicle to a halt. Disc brakes are generally more effective than drum brakes, especially in terms of heat dissipation, which is crucial during prolonged braking. This efficiency makes them the preferred choice in most modern vehicles, particularly in the front brakes, where the majority of stopping power is required.
Key Advantages of Disc Brakes
One of the primary advantages of disc brakes is their superior performance in wet conditions. The exposed nature of the disc allows water to quickly dissipate, maintaining effective braking ability even when the roads are slick. In contrast, drum brakes can retain water and debris, which may hinder their performance. Additionally, disc brakes are less prone to brake fade, a phenomenon where the brakes overheat and become less effective due to prolonged use. This attribute makes disc brakes more reliable for high-performance vehicles and heavy-duty applications.
brake drums or discs must
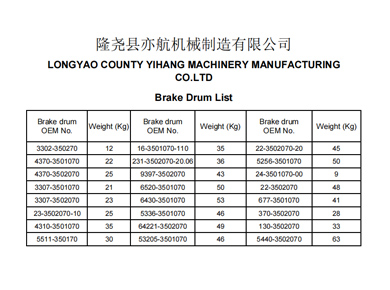
Maintenance is another crucial factor in the longevity and performance of brake systems. Disc brakes are generally easier to inspect and replace than drum brakes. When checking disc brakes, technicians can easily see the condition of the rotor and pads, allowing for timely maintenance and replacement. Drum brakes, however, require removing the drum to inspect the shoes, which can be more labor-intensive and time-consuming.
Signs of Wear and When to Replace
Regardless of whether a vehicle uses brake drums or discs, the critical point is to pay attention to signs of wear. For disc brakes, common indicators include squeaking or grinding noises, a pulling sensation to one side when braking, or a dashboard warning light. For drum brakes, you might notice a similar pulling sensation or decreased responsiveness. As a general rule, brake pads should be replaced every 25,000 to 70,000 miles, while rotors usually last longer but should be inspected regularly.
Neglecting brake maintenance can lead to severe consequences, including increased stopping distances, brake failure, or even accidents. Therefore, keeping up with regular inspections and adhering to manufacturer recommendations for replacements is vital for maintaining vehicle safety.
Conclusion
In summary, both brake drums and discs play essential roles in vehicle braking systems, with disc brakes often providing superior performance and ease of maintenance. Understanding the differences and monitoring the condition of these components can significantly enhance vehicle safety. Remember, the brakes are one of the most critical safety features of any vehicle, and regular care and maintenance are indispensable in ensuring they function correctly when needed. By prioritizing brake health, drivers can enjoy safer journeys on the road, reducing the risk of accidents caused by brake failure.
-
Brake Drum Man - High-Quality Drum Brake Drums & Brake Shoes for Reliable Performance
NewsJun.24,2025
-
High-Quality Brake Drum Kamaz – Durable Drum Brake Drum & Brake Shoe Replacement
NewsJun.10,2025
-
High-Quality Brake Drum Liza for Drum Brake Systems - Superior Durability and Performance
NewsJun.10,2025
-
High-Quality Brake Drum Kamaz – Durable Drum Brake Drum & Brake Shoe Solutions
NewsJun.10,2025
-
Durable Kamaz Brake Drums High-Performance Truck Parts
NewsJun.09,2025
-
Premium Brake Drum Maz Kit with Shoes Enhanced Braking
NewsJun.09,2025
