Aug . 20, 2024 20:31 Back to list
Understanding the Definition and Function of Brake Drums in Automotive Systems
Understanding Brake Drums Definition and Functionality
Brake drums are an essential component of a vehicle's braking system, particularly in older cars and trucks where drum brakes were more common. Although many modern vehicles have transitioned to disc brakes, brake drums remain prevalent in various applications due to their effectiveness and reliability. To comprehend their importance, it is crucial to explore what brake drums are, how they function, and their advantages and disadvantages.
At its core, a brake drum is a cylindrical component that houses the brake shoes and is attached to the wheel hub. When the brake pedal is pressed, hydraulic pressure is transmitted to the brake shoes, forcing them against the inner surface of the drum. This contact generates friction, which slows down the rotation of the wheel, ultimately bringing the vehicle to a stop. The design of the brake drum allows for a larger surface area compared to some disc brake systems, which can result in more effective braking in certain conditions.
Understanding Brake Drums Definition and Functionality
Another advantage of brake drums is their cost-effectiveness. In general, drum brakes are less expensive to manufacture and install than their disc counterparts. This is particularly advantageous for budget-conscious consumers or for vehicles designed to carry heavy loads, such as trucks and vans, where cost-efficiency is crucial.
brake drums definition
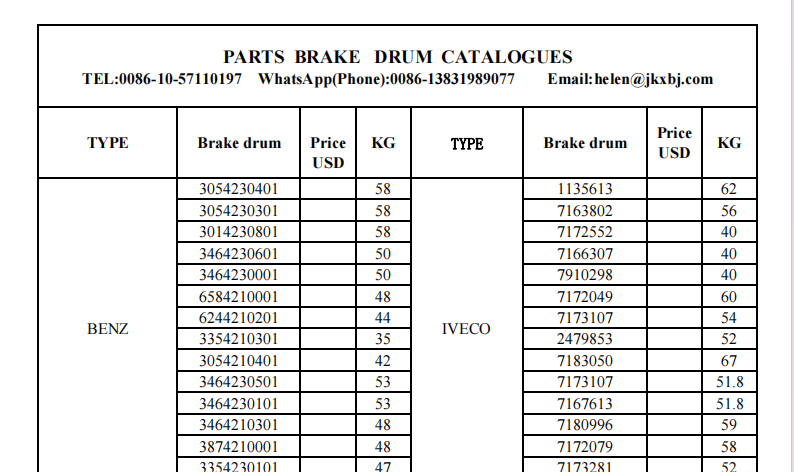
However, brake drums are not without their drawbacks. One significant disadvantage is their weight. Brake drums are typically heavier than disc brakes, which can contribute to the overall weight of the vehicle and affect fuel efficiency. Furthermore, drum brakes can be more challenging to service. When the brake shoes wear down, accessing them for replacement often requires removing the entire brake drum, a more labor-intensive process than changing brake pads on disc brakes.
Another issue associated with drum brakes is the potential for water and debris to accumulate inside the drum, which can compromise braking effectiveness. Moisture can lead to corrosion, and dirt can cause the brake shoes to stick, resulting in uneven wear and reduced performance.
Despite these disadvantages, many vehicles still utilize brake drums, particularly in rear braking systems where the load is lighter compared to the front. Depending on the application, the durability and functionality of brake drums can be sufficient for everyday driving needs. They remain an integral part of the braking systems in many older vehicles and heavier-duty applications.
In summary, brake drums play a vital role in the braking systems of various vehicles. Their ability to generate friction for effective stopping power, along with their heat management capabilities, make them a valuable option, especially in certain contexts. While they come with their own set of challenges—such as heavier weight and maintenance requirements—brake drums continue to be a practical choice for numerous applications. Understanding their definition and functionality not only highlights their role in vehicle safety but also emphasizes the ongoing need for diverse braking technologies in the automotive industry.
-
Brake Drum Man - High-Quality Drum Brake Drums & Brake Shoes for Reliable Performance
NewsJun.24,2025
-
High-Quality Brake Drum Kamaz – Durable Drum Brake Drum & Brake Shoe Replacement
NewsJun.10,2025
-
High-Quality Brake Drum Liza for Drum Brake Systems - Superior Durability and Performance
NewsJun.10,2025
-
High-Quality Brake Drum Kamaz – Durable Drum Brake Drum & Brake Shoe Solutions
NewsJun.10,2025
-
Durable Kamaz Brake Drums High-Performance Truck Parts
NewsJun.09,2025
-
Premium Brake Drum Maz Kit with Shoes Enhanced Braking
NewsJun.09,2025
